Since the beginning of the twenty-first century, competition has intensified across the globe. In the wake of this, designers have the opportunity to incorporate innovation into their products. Automating the functioning of the products is one way for these designers to infuse innovation into their work.
Tweaking a product’s operations, designers either chose automation devices already available on the market or created new devices for automation. Automating devices usually involve connecting and disconnecting electrical circuits by turning them on and off to manage their operations. Electrical circuits are connected and disconnected for the most part using electromechanical relays in this type of automation. This guide is all about electromechaniclal relay in detail.
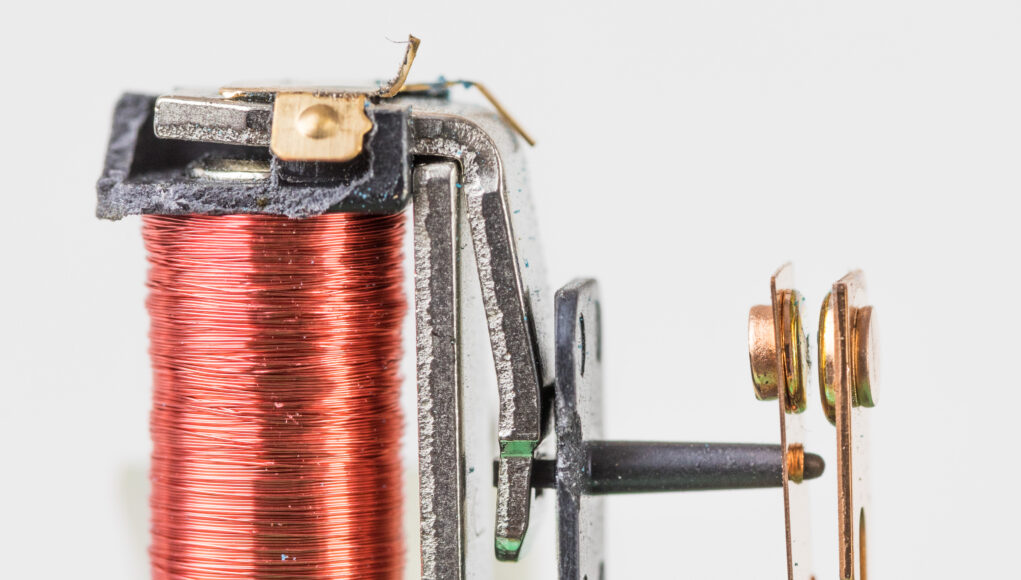
An Electromechanical Relay is a switch commonly used in electrical and electronic systems to control power or signal circuits. It comprises a coil, a movable armature, and a set of contacts. When a voltage is applied to the coil, it creates a magnetic field that pulls the armature towards the coil, closing the contacts and completing the circuit. When the voltage is removed, the spring forces the armature back to its original position, opening the contacts and breaking the circuit.
Electromechanical relays are popular due to their ability to switch large currents and voltages, durability and reliability, and low cost compared to other types of switches. They are commonly used in power supplies, motor control, lighting, and automation systems. However, their mechanical nature limits their switching speed, and they can be affected by shock, vibration, and environmental factors, which may require additional protective measures.
What is an electromechanical relay?
In its simplest form, an electromechanical relay is a switch. More precisely, it is a switch that is operated by electricity. When a low-power signal controls a circuit, relays are used to control several circuits or a signal that controls multiple circuits at once. There are several types of electromechanical relays, and which type is used in each device is determined by its function.
Some relays generate magnetic fields using electromagnets or magnets powered by electricity, and the magnetic fields disappear when the electricity is turned off. An electric current consists of a charge of electricity flowing through it. As the name implies, a contactor controls high-power devices such as electric motors.
What are the most common types of electromechanical relays?
There are several types of electromechanical relays, each classified according to its application and construction:
1. The Reed Relay
A solenoid is fitted with a switch. To protect against corrosion, the switch contacts are enclosed in glass or ceramic ducts. They are magnetic contacts that are affected by the solenoid’s field. A reed contact has a fast switching mechanism and draws only a tiny amount of power from the control circuit, but it must be maintained regularly.
Several applications involving radiofrequency switching and microwave switching require Reed relays. They are suitable for circuits requiring a low current operation.
Read more:What Are MCBs? Its Types, Working, Operation, And Applications With Description
2. Relay for Heavy Duty
These electromechanical relays have convertible contacts (which can be operated either normally open or normally closed by changing terminal bolts and shifting components 180 degrees). Heavy-duty relays are used in machine control and other industrial applications in addition to being operated by coils. In general, these relays have a long life and can be easily maintained.
3. The general-purpose relay
There are mechanical contacts on this type of relay that are activated by a magnetic coil. An electromagnet inside the relay coil is energized when the terminals from the relay coil are connected to the main road, which generates a magnetic field that pulls the armature downward with a spring; the contact between the relay coil and the main load is broken.
General-purpose relays are easy to troubleshoot and usually inexpensive, making them ideal for commercial and industrial uses where cost and handling are critical factors. Due to their plug-in features, most of these relays can be replaced quickly and troubleshoot easily.
Pros of electromechanical relays
Electromechanical relays have a number of advantages in control circuits. They include:
- AC and DC contacts can be switched.
- The unit is inexpensive to purchase.
- The unit is easy to mount.
- The unit has a shallow contact voltage drop, so a heat sink is unnecessary.
- The unit has a high voltage transient resistance.
- Off-State current leakage is not present through open contacts.
Cons of electromechanical relays
Relays with electromechanical contacts have some shortcomings. Below are some of them:
- The process is relatively slow.
- They have a low isolation voltage.
- Age-related changes in characteristics.
- The contact life is short in applications during which rapid switching or high loads are used.
- The contacts generally struggle to switch high inrush currents.
Usage of electromechanical relay
Switches convert small amounts of power into large amounts using a small amount of energy. A typical household appliance containing relays is a hairdryer, a kitchen appliance, and a light switch that must be switched on and off. Likewise, they are used in cars when something needs to be turned off or on. Relay panels make maintenance easier in fuse boxes, and modern car manufacturers use them in fuse boxes. The selection of relays for modern devices should be based on a few factors.
Prior to making a contact, one must decide if it will be normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO). Depending on the relay type and whether or not the device must remain on all the time or be toggled back and forth between on and off, the relay type will be needed. The maximum voltage that can be handled by the armature and its contact devices should be considered as well. In addition, one of the most critical considerations is what voltage and current will be required for the electronics project since this will determine how the armature operates.
What are the Key features of an Electromechanical Relay?
Electromechanical relays can be equipped with a variety of unique characteristics, which include:
- Convertible contacts allow you to adjust the contact orientation. For example, you can convert an open contact to a closed one and vice versa.
- Relays that are current- and voltage-sensitive can alert you when a maximum current or voltage thresholds have been reached.
- With expandable deck relays, additional switch poles can be added.
- Intrinsically safe relays will not produce sparks or other thermal effects when used with gas mixtures that may ignite. They are frequently found in explosion-proof applications.
- Devices that use a pushbutton for manual testing of relay circuits are called push-to-test devices.
- The speeds of time delay relays can be adjusted, allowing them to delay times when they make or break.
Applications of electromechanical relay
The following are some applications of electromechanical relays.
- They are used to protect electric systems with AC and DC power.
- Large power loads are controlled with them in industrial operations.
- They are used in motor control and automotive applications.
In an electromechanical relay, the output component’s contacts are connected using a real-world moving part. The circuit containing the high-power signal can be closed by moving this contact using electromagnetic forces produced by the low-power input signal.
Relay: an electromechanical or electronic device?
A relay is an electromagnetically operated mechanical device that uses a magnetizing current to open or shut electrical connections.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the purpose of an electromechanical relay?
Electromechanical relays are used for multiple purposes. The primary purpose is to switch large electrical loads using a low-voltage control circuit. This is accomplished by reducing the voltage level from a high level to that used for control.
How are electromechanical overcurrent relays operated?
When a control signal is applied to an electromechanical relay, the coil generates a magnetic field and the relay functions. It has moving contacts in its output circuit, which makes it an electromechanical device. Electrical signals are used to operate the contacts.